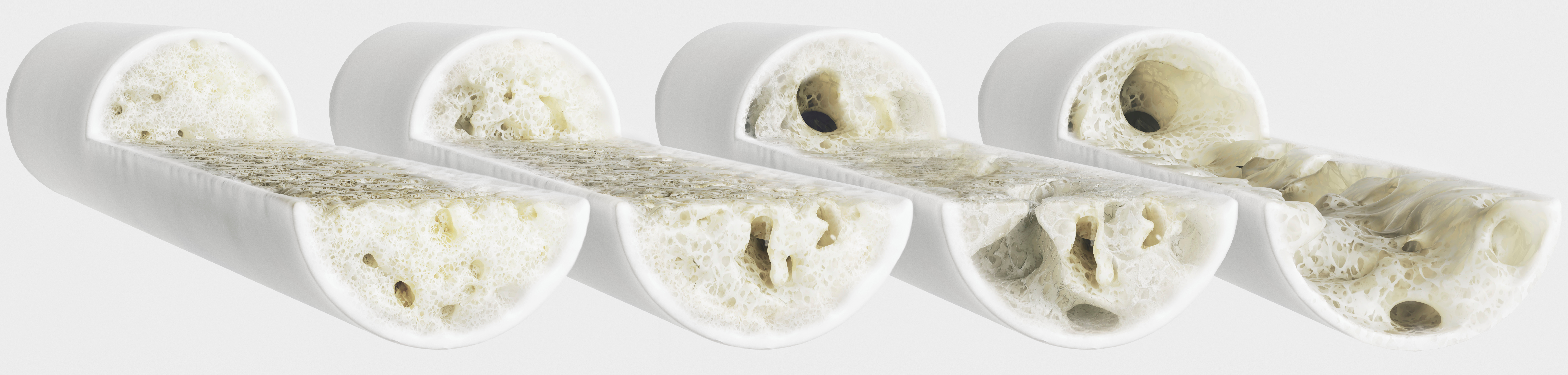
Osteoporosis is a disease that occurs when bone density and/or the quality of your bone decreases, causing weak bones. It occurs when the density and quality of bone are reduced. Normally, bones go through a process called “Remodeling” where old bone is broken down and new bone is built in its place. However, in osteoporosis, the creation of new bone is unable to keep pace with the removal of old bone, resulting in a net loss of bone mass.
Who is at risk for Osteoporosis?
There are several clinic risk factors that can contribute to the development of osteoporosis including:
- Age: Around the age of 40, the bone building part of the remodeling process begins to slow down which results in a net loss over time. This imbalance becomes even more prevalent after menopause.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men due to hormonal changes during menopause.
- Genetics: A family history of osteoporosis can increase the risk.
- Hormonal changes: Low estrogen levels in women and low testosterone levels in men can lead to bone loss.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits and Vitamin Deficiencies: Lack of physical activity, a diet poor in calcium and vitamin D, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications can all contribute to bone loss.
- Medical Conditions: Some medical conditions, such as celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and hormonal disorders, can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Medications: Long-term use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids and some anticonvulsants, can weaken bones.
Each of these, especially when compounded, can ultimately result in a fracture or at minimum, an increased risk of fracture which can occur even with minor trauma or stress on the bones. The most common sites of an osteoporotic fracture are wrists, hip, and spine. Fractures, particularity those of the hip, have potential for serious consequences for older adults and can lead to decreased mobility and independence.
How is Osteoporosis Prevented and Managed?
Preventing and managing osteoporosis typically involves lifestyle changes including adopting a nutrient dense diet and vitamin regimen, regular weight-bearing exercise, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, and possible medication management. It is important to know this is a lifelong diagnosis with several possible treatment pathways that are individualized to each patient. A detailed interview along with imaging and labs will help determine treatment recommendations.
Regular bone density testing can help diagnose osteoporosis early and help guide the treatment process as well. Early detection and proactive management are essential in reducing the risk on further onset and the risk of potential fractures.
What is Bone Density?
Bones density, also known as Bone Mineral Density, is the total amount of bone mineral within boney tissue. Bone Density is measured using low-dose x-ray tests called DEXA or DXA scans that measure calcium and additional minerals within the bones. This measurement helps determine the strength and thickness (density) of bone which then helps providers predict a patient’s fracture risk.
Stay tuned as we continue our Bone Health series and further discuss treatment methods, FRAX scores, and much more.
